This is for informational purposes only. For medical advice or diagnosis, consult a professional.
digital Nerve Graft: Bridging the Gap
Digital nerve grafts are a surgical technique used to repair severed or damaged nerves in the fingers and hands. These delicate nerves are crucial for sensation, allowing us to feel temperature, pressure, and pain. When injured, they can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, affecting their ability to perform everyday tasks and even causing chronic pain.
This article will delve into the intricacies of digital nerve grafts, exploring the underlying principles, surgical procedures, and the road to recovery.
Understanding Nerve Injury
Before we delve into the specifics of digital nerve grafts, it’s essential to understand how nerve injuries occur.
Trauma: This is the most frequent cause, including lacerations, crush injuries, and penetrating wounds from accidents, falls, or even glass.
Neurapraxia: The mildest form, where the nerve is temporarily disrupted but the nerve fibers remain intact. Recovery usually occurs spontaneously.
The Role of Nerve Grafts
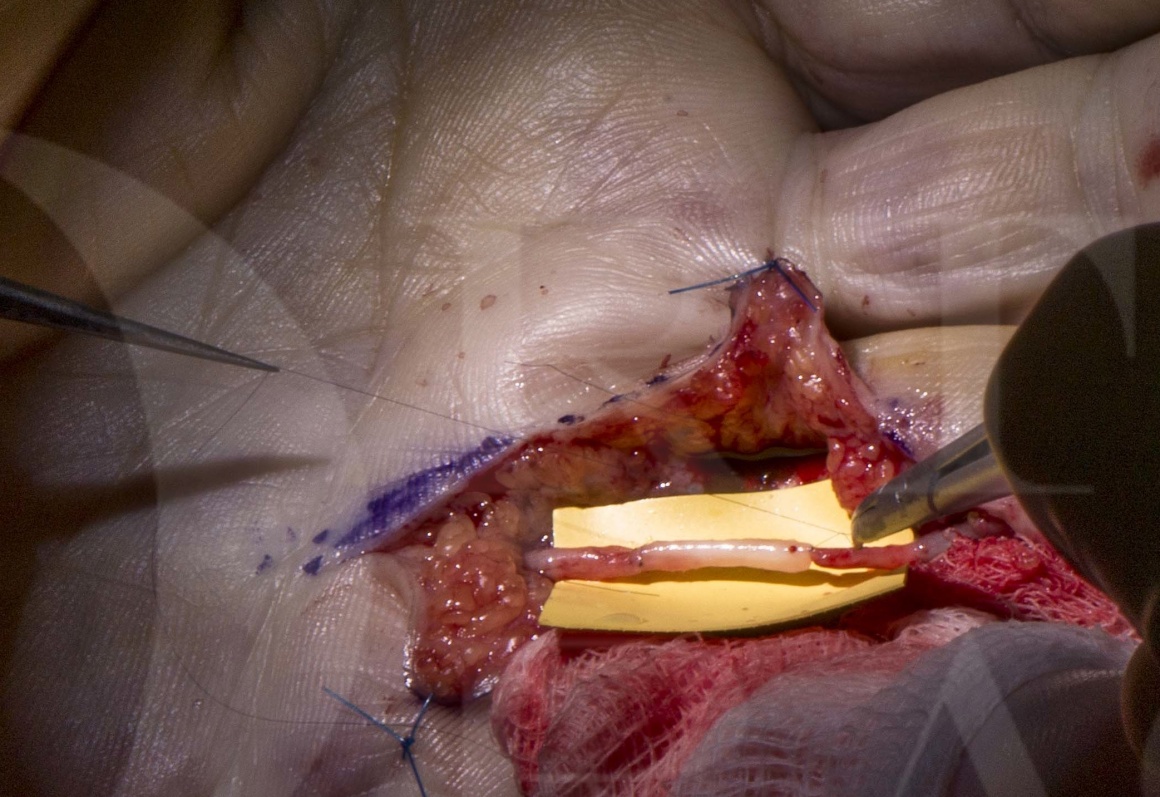
When a nerve is severed, the natural ability of the body to regenerate the nerve fibers may be hindered or impossible. This is where nerve grafts come into play. A nerve graft is a surgical procedure where a segment of healthy nerve tissue is harvested from another part of the body and used to bridge the gap between the severed ends of the damaged nerve.
Autograft: This is the most common type, where the graft is taken from another part of the patient’s own body, typically a sensory nerve in the leg or arm.
The Surgical Procedure
Digital nerve graft surgery is a delicate and complex procedure typically performed by a microsurgeon under a powerful operating microscope.
1. Harvesting the Graft: If an autograft is used, the surgeon will carefully harvest a segment of healthy nerve from the donor site.
2. Preparing the Nerve Ends: The surgeon meticulously prepares the ends of the injured nerve, removing any damaged tissue and ensuring a clean surface for the graft.
3. Grafting: The harvested nerve graft is then precisely sutured to the two ends of the injured nerve, bridging the gap.
4. Immobilization: The affected area is typically immobilized for several weeks to allow for proper healing and nerve regeneration.
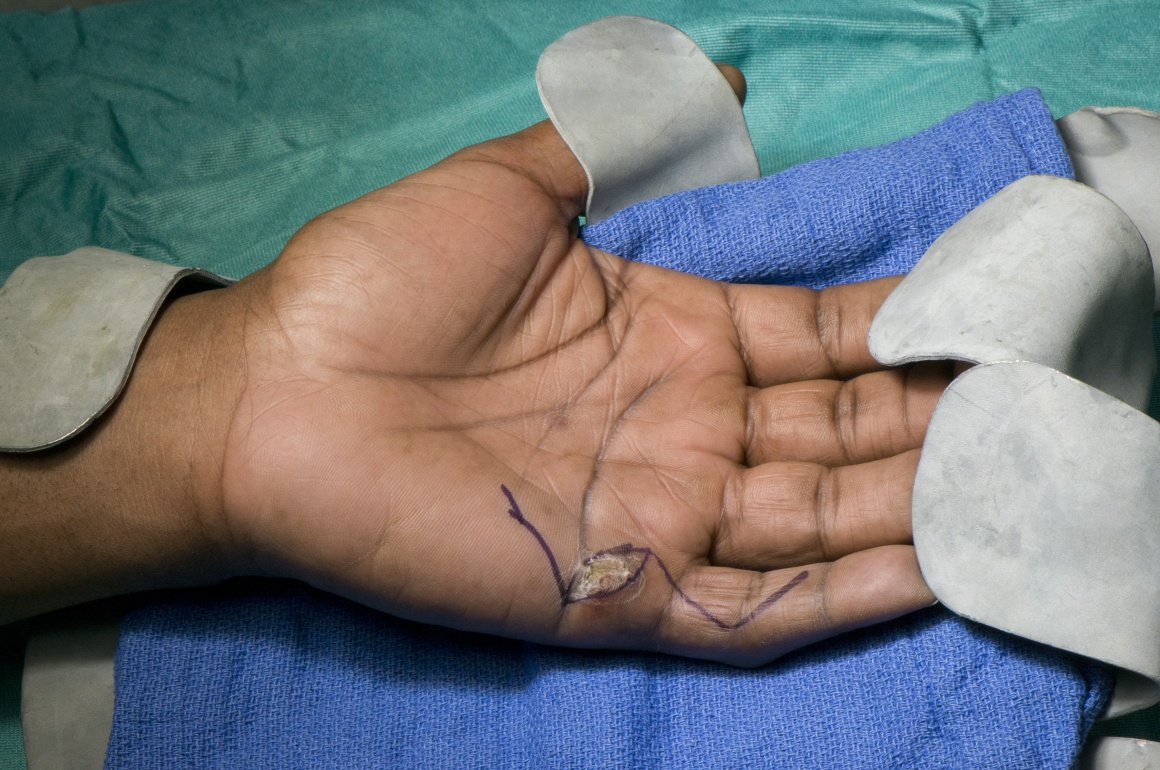
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after a digital nerve graft is a gradual process. Nerve regeneration occurs at a rate of approximately 1 millimeter per day.
Pain Management: Pain medication is often prescribed to manage post-operative discomfort.
Potential Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with digital nerve grafts, including:
Infection:
Success Rates
The success of a digital nerve graft varies depending on several factors, including the severity of the injury, the length of the nerve gap, and the overall health of the patient.
Age: Younger patients generally have better outcomes.
Conclusion
Digital nerve grafts are a complex but potentially life-changing surgical procedure for individuals with severe nerve injuries in the hand. While recovery can be a lengthy process, advancements in surgical techniques and rehabilitation strategies have significantly improved outcomes for many patients.
If you or someone you know has suffered a digital nerve injury, it is essential to seek professional medical advice from a qualified hand surgeon. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the chances of a successful recovery and return to normal function.
digital nerve graft
